Now Practice WBSSC SLST Education Mock Test on the Psychological Foundation of Education with MCQ answers. Boost your SSC Education preparation with real exam-level questions for WBSSC School Service aspirants.
SLST Education Mock Test with Answers | Psychological Foundation of Education
This section of the SLST Education syllabus focuses on the core psychological principles that influence education. This mock test has been specially curated to help SLST aspirants evaluate their grasp of these psychological fundamentals and boost their confidence before the final exam.
Syllabus
II. Psychological Foundations of Education
a) Growth and development – Growth and development of the child Stages and areas of development. Physical, Cognitive, Social development up to the stage of Adolescence.
b) Intelligence – Concept and Two-factor theory.
c) Personality – Concept and Trait theory.
d) Learning – Theories of Learning –Connectionism (Thorndike, Pavlov, Skinner) and Cognitive (Gestalt). Factors affecting Learning: Maturation, Interest and Motivation, Memory, and Attention.
a) Growth and development – Growth and development of the child Stages and areas of development. Physical, Cognitive, Social development up to the stage of Adolescence.
Q. Which of the following best describes “Growth”?
A. Qualitative change
B. Change in personality
C. Increase in height and weight
D. Development of values
Q. Development is –
A. Quantitative only
B. Qualitative only
C. Both qualitative and quantitative
D. Physical only
Q. The span of adolescence usually ranges from
A. 6–10 years
B. 12–19 years
C. 2–6 years
D. 20–25 years
Q. In which stage do children begin symbolic thinking according to Piaget?
A. Sensorimotor
B. Preoperational
C. Concrete operational
D. Formal operational
Q. In which stage does abstract thinking begin to emerge according to Piaget?
A. Sensorimotor
B. Preoperational
C. Concrete operational
D. Formal operational
Q. Which is NOT an area of development?
A. Physical
B. Emotional
C. Magical
D. Social
Q. The rate of physical growth is fastest during
A. Adolescence
B. Infancy
C. Childhood
D. Adulthood
Q. What does the Cephalocaudal trend in development mean?
A. Development from center to outer
B. Development from foot to head
C. Development from head to foot
D. Simultaneous development
Q. Which development pattern is first noticed in prenatal development?
A. Proximodistal
B. Spiral
C. Cephalocaudal
D. Horizontal
Q. Proximodistal development refers to
A. Development from toes to brain
B. Development from outer parts to center
C. Development from center to extremities
D. Irregular growth
Q. Which of the following is a principle of development?
A. Development is irregular
B. Development is unpredictable
C. Development proceeds from general to specific
D. Development stops at adolescence
Q. Which is a characteristic of development?
A. It is fixed
B. It varies in all individuals
C. It is same for all
D. It is instant
Q. Growth refers to –
A. Physical increase only
B. Mental maturity
C. Overall personality
D. Spiritual development
Q. What is the difference between growth and development?
A. Growth is qualitative, development is quantitative
B. Growth is reversible
C. Growth is physical, development is holistic
D. Growth continues lifelong
Q. Maturation refers to
A. Acquiring new skills
B. Natural unfolding of genetic potential
C. Reading books
D. Parental training
Q. Which of the following is an emotional characteristic of adolescence?
A. Balanced behavior
B. Stability of mind
C. Mood swings and anxiety
D. Lack of imagination
Q. During childhood, language development is part of –
A. Physical development
B. Emotional development
C. Cognitive development
D. Social development
Q. Adolescents are highly influenced by
A. Teachers
B. Parents
C. Peers
D. Media
Q. Which principle of development suggests “Every individual develops at their own pace”?
A. Principle of general to specific
B. Principle of uniformity
C. Principle of individual differences
D. Principle of hierarchy
Q. Which of the following statements is true about development?
A. All children develop at the same rate
B. Development ends in adolescence
C. Development is affected by both heredity and environment
D. Development is only mental
Q. During adolescence, children undergo
A. Only cognitive changes
B. No changes
C. Physical, emotional and cognitive changes
D. Only physical growth
Q. Which stage of development is considered as “the foundation of personality”?
A. Adolescence
B. Infancy
C. Early childhood
D. Late adulthood
Q. Which domain of development is involved in learning to speak and read?
A. Physical
B. Emotional
C. Cognitive
D. Social
🧠 Intelligence: Concept and Two-Factor Theory
🔹 Concept of Intelligence
Intelligence refers to the mental capacity to learn, reason, solve problems, and adapt to new situations.
📘 Binet (1905) defined intelligence as –
“The capacity to judge well, to understand well, and to reason well.”
📘 Wechsler (1944) said that –
“Intelligence is the aggregate or global capacity of an individual to act purposefully, to think rationally, and to deal effectively with the environment.”
🔹 Two-Factor Theory of Intelligence (Charles Spearman, 1904)
Spearman introduced this theory based on factor analysis. He proposed that intelligence consists of two components:
- General Factor (g-factor)
- Represents general mental energy or overall intelligence.
- Common in all cognitive tasks like reasoning, memory, comprehension.
- If a person is good in one area, they tend to do well in others due to the g-factor.
- Specific Factor (s-factor)
- Unique to each particular task (e.g., math skill, language ability).
- Explains individual variations in specific subjects.
🔹 Equation:
Intelligence = g + s
Where –
- g = General intelligence
- s = Specific abilities in particular domains
🔹 Example:
A student may have high g-factor (good overall reasoning skills) but weak s-factor in mathematics.
🔹 Importance of Two-Factor Theory:
- First scientific theory explaining the structure of intelligence.
- Foundation for modern IQ testing and psychometric analysis.
- Helped separate innate general ability from subject-specific learning.
Q. Who defined intelligence as “the capacity to learn and adjust in new situations”?
A. Thorndike
B. Binet
C. Piaget
D. David Wechsler
Q. Who developed the first practical intelligence test in 1905?
A. David Wechsler
B. Lewis Terman
C. Alfred Binet
D. Arthur Jensen
Q. What does IQ stand for?
A. Intelligence Quotient
B. Instruction Quotient
C. Inherited Quotient
D. Intention Quotient
Q. What is the formula for calculating IQ in the Binet–Simon scale?
A. (Mental Age / Chronological Age) × 100
B. (Chronological Age / Mental Age) × 100
C. (Mental Age + Chronological Age) ÷ 2
D. (Mental Age – Chronological Age) × 100
Q. Whose test is called WAIS?
A. Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale
B. Weschler Analytical Intelligence Scale
C. Wide Aptitude Intelligence Scale
D. World Advancement Intelligence Scale
Q. Which psychologist believed intelligence includes verbal IQ and performance IQ?
A. Sternberg
B. Gardner
C. Wechsler
D. Binet
Q. Sternberg’s Triarchic Theory includes all except
A. Analytical intelligence
B. Practical intelligence
C. Creative intelligence
D. Spiritual intelligence
Q. What type of intelligence helps in understanding others’ feelings?
A. Intrapersonal
B. Interpersonal
C. Logical
D. Linguistic
Q. Understanding and managing one’s own emotions refers to
A. Interpersonal skills
B. Intrapersonal intelligence
C. Cognitive control
D. Emotional suppression
Q. Emotional Intelligence was popularized by
A. Piaget
B. Goleman
C. Wechsler
D. Terman
Q. A high IQ does not necessarily mean
A. High creativity
B. Logical reasoning
C. Academic success
D. Verbal skill
Q. Gifted children are usually defined as those with IQ above
A. 85
B. 100
C. 115
D. 130
Q. Which theory views intelligence as a single global construct?
A. Spearman’s Two-Factor
B. Gardner’s Multiple Intelligences
C. Binet’s Singular Theory
D. Sternberg’s Three-Factor
Q. Social intelligence includes
A. Grammar rules
B. Understanding social situations
C. Mechanical reasoning
D. Facial recognition exclusively
Q. Which of the following is a group intelligence test?
A. Stanford–Binet
B. Wechsler Intelligence Scale
C. Army Alpha Test
D. WPPSI
Q. The main purpose of an intelligence test is to
A. Measure emotional stability
B. Assess cognitive ability
C. Improve memory
D. Diagnose personality disorder
Q. Stanford–Binet test is mainly used for
A. Adults
B. Children
C. Group testing
D. Hearing test
Q. The most important feature of a good intelligence test is
A. Cost
B. Speed
C. Validity
D. Presentation
Q. The IQ score of a person with mental age 10 and chronological age 8 is –
A. 80
B. 100
C. 120
D. 125
Q. Who proposed the Two-Factor Theory of Intelligence?
A. Howard Gardner
B. Alfred Binet
C. Charles Spearman
D. J.P. Guilford
Q. In which year was the Two-Factor Theory proposed?
A. 1910
B. 1904
C. 1925
D. 1938
Q. Which journal first published Spearman’s theory?
A. British Journal of Psychology
B. Psychological Review
C. The American Journal of Psychology
D. Child Development
Q. What does the “g” factor in Spearman’s theory stand for?
A. General education
B. Group behavior
C. General intelligence
D. Genetic capacity
Q. What does the “s” factor represent in the Two-Factor Theory?
A. Special learning disorder
B. Specific intelligence in certain tasks
C. Social adaptation
D. Speed of memory
Q. What statistical method did Spearman use to develop his theory?
A. T-test
B. Chi-square
C. Correlation coefficient
D. Factor analysis
Q. Which of the following best explains Spearman’s equation?
A. Intelligence = Aptitude + Environment
B. Intelligence = g + s
C. IQ = Mental Age / Chronological Age
D. Learning = Motivation × Ability
Q. Which of the following is NOT true about Spearman’s theory?
A. Intelligence has one general core
B. Specific abilities are the same for all people
C. General intelligence influences all mental tasks
D. Each task requires its own specific ability
Q. Who criticized Spearman’s theory and proposed multiple intelligences instead?
A. Alfred Binet
B. Robert Sternberg
C. J.P. Guilford
D. Howard Gardner
Q. A student performing well in all subjects is likely to have high
A. “s” factor
B. General intelligence
C. Emotional intelligence
D. Motor ability
Q.
Q. Which of the following represents the Tetrad Equation used by Spearman in his intelligence theory?
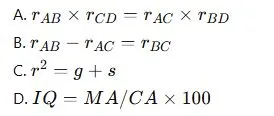
Q. Who popularized the concept of Emotional Intelligence (EI)?
A. Alfred Binet
B. Daniel Goleman
C. Howard Gardner
D. Charles Spearman
Q. Emotional Intelligence helps individuals to
A. Score better on IQ tests
B. Handle interpersonal relationships effectively
C. Learn faster
D. Avoid studying
Q. Emotional intelligence is mostly developed through
A. Exams
B. Self-reflection and social experience
C. IQ training
D. Vocabulary building
Personality – Concept and Trait theory.
Q. Who defined personality as “the dynamic organization within the individual of those psychophysical systems that determine his unique adjustments to his environment”?
A) Freud
B) Allport
C) Jung
D) Eysenck
Q. Which theory of personality focuses on identifying measurable traits that differ among individuals?
A) Psychoanalytic Theory
B) Behaviorist Theory
C) Trait Theory
D) Humanistic Theory
Q. According to Eysenck, how many basic dimensions of personality are there?
A) Two
B) Three
C) Four
D) Five
Q. The Big Five Personality Traits do NOT include
A) Openness
B) Conscientiousness
C) Empathy
D) Neuroticism
Q. Which test is a projective technique used for assessing personality?
A) MBTI
B) Rorschach Inkblot Test
C) EPQ
D) MMPI
Q. According to Freud, which part of personality operates on the reality principle?
A) Id
B) Ego
C) Superego
D) Shadow
Q. The term “trait” in personality psychology refers to
A) A temporary emotion
B) A stable characteristic
C) An unconscious motive
D) A defense mechanism
Q. Which personality type, according to Carl Jung, is focused inward and prefers solitude?
A) Extrovert
B) Ambivert
C) Introvert
D) Neurotic
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the Psychological Foundation of Education is essential for every teaching aspirant appearing in the SLST examination.
This mock test serves as a comprehensive practice tool, helping candidates reinforce key concepts and evaluate their exam preparedness.
By practicing such questions, candidates can better understand the theoretical and applied aspects of educational psychology — a foundation that strengthens both professional competence and classroom effectiveness.
References
- Kar. Chintamani, Exceptional Children Their Psychology and Education. Sterling Publication Pvt. Ltd. New Delhi.
- Kirk, S. A. Educating Exceptional Children. Oxford IBH. New Delhi.
- Mangal, S. K. Educating Exceptional Children: An Introduction to Special Education. PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd. New Delhi.
- Panda, K. C. Education of Exceptional Children. Vikas Publishing House Pvt. Ltd. New Delhi.
- Internet sources
Q – What is meant by psychological foundations of education?
Ans. – Psychological foundations of education refers to the application of psychological principles to understand and improve teaching, learning, and student behavior.
Q. Why is educational psychology important for teachers?
Ans. – Educational psychology helps teachers understand student needs, learning patterns, motivation, and how to manage the classroom effectively.





